PUBLICATIONS (24-1) – 2015~
PUBLICATIONS-2015
- Schmidt, N.W.#, Jin, F.#, Lande, R., Curk, T., Xian, W., Lee, C., Frasca, L., Frenkel, D., Dobnikar, J.*, Gilliet, M.*, Wong, G.C.L.* (2015). Liquid-crystalline ordering of antimicrobial peptide-DNA complexes controls TLR9 activation. Nat. Mater., 14, 696 – 701.
PUBLICATIONS-2014
- Zhang, R.#, Ni, L.#, Jin, Z., Li, J., Jin, F.* (2014). Bacteria slingshot more on soft surfaces. Nat. Commu., 5, 5541.
- Gao, P., Xing, X., Li, Y., Ngai, T., Jin, F.* (2014). Charging and discharging of single colloidal particles at oil/water interfaces.Sci. Rep., 4, 4778.
PUBLICATIONS-2013
- Zhao, K., Tseng, B., Beckerman, B., Jin, F. , Gibiansky, M.L., Harrison, J., Luijten, E. *, Parsek, M. *, Wong, G.C.L.* (2013). Psl trails guide exploration and microcolony formation in early P. aeruginosa biofilms. Nature, 497, 388-392.
- Liu, T., Hu, J., Jin, Z., Jin, F. *, Liu, S. Y.* (2013). Two-Photon ratiometric fluorescent mapping of intracellular transport pathways of pH-responsive block copolymer micellar nanocarriers. Adv. Heal. Mater., 2, 1576-1581.
- Hu, J., Liu, T., Jin, Z., Jin, F. *, Liu, S. Y.* (2013). Synergistically enhance magnetic resonance/fluorescence imaging performance of responsive polymeric nanoparticles under mildly acidic biological milieu. Mac. Rap. Comm., 34, 9.
PUBLICATIONS-2011
- Jin, F. #, Conrad, J.C.#, Gibiansky, M.L., Wong, G.C.L.*(2011). Bacteria use type-IV pili to slingshot on surfaces. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA , 108, 12617-12622.
- Yue, Y.*, Jin, F. , Deng, R., Cai, J., Dai, Z., Lin, M.C., Kung, H.F., Mattebjerg, M.A., Andresen, T.L., Wu, C.*(2011). Revisit complexation between DNA and polyethylenimine −Effect of length of free polycationic chains on gene transfection. J. Control. Release., 152, 143.
- Conrad, J.C.#, Gibiansky, M.L.#, Jin, F. , Gordon, V.D. Motto, D.A., Mathewson, M.A., Stopka,W.G., Zelasko, D.C., Shrout, J.D., Wong, G.C.L.*(2011). Flagella and pili-mediated near-surface single-cell motility mechanisms in P. aeruginosa. Biophysical J, 100, 1608.
PUBLICATIONS-2010
- Gibiansky, M.L.#, Conrad, J.C.#, Jin, F. , Gordon, V.D. Motto, D.A., Mathewson, M.A., Stopka,W.G., Zelasko, D.C., Shrout, J.D., Wong, G.C.L.*(2010). Bacteria use type-IV pili to walk and detach from surfaces. Science, 330, 197.
- Yue, Y.*, Jin, F. , Deng, R., Cai, J., Chen, Y., Lin, M.C., Kung, H.F., Wu, C.*(2010). Revisit complexation between DNA and polyethylenimine −Effect of uncomplexed chains free in the solution mixture on gene transfection. J Control Release, 155(1), 67-76.
- Deng, R., Diao, S, Yue, Y., Ngai, T., Wu, C.,Jin, F. *(2010). Dynamic and structural scalings of the complexation between pDNA and bPEI in semidilute and low-salt solutions. J Control Release, 93(6), 571.
PUBLICATIONS-2009
- Deng, R.*, Yue, Y., Jin, F. , Chen, Y., Kung, HF., Lin, MC., Wu, C.(2009). Revisit the complexation of PEI and DNA – how to make low cytotoxic and highly efficient PEI gene transfection non-viral vectors with a controllable chain length and structure? J Control Release, 140(1), 40.
- Ge, H., Jin, F. , Li, JF., Wu, C.*(2009). How Much Force Is Needed To Stretch a Coiled Chain in Solution? Macromolecules, 42, 4400.
PUBLICATIONS-2008
- Jin, F. , Gong, XJ., Ye, J., Ngai, T.*(2008). Direct measurement of nanobubble-induced weak depletion attraction between a spherical particle and a flat surface in an aqueous solution. Soft Matter, 4, 968.
- Ngai, T*., Xing, XC.,Jin, F. (2008). Depletion Attraction between a Polystyrene Particle and a Hydrophilic Surface in a Pluronic Aqueous Solution. Langmuir, 24(24), 13912.
- 35. Hong, LZ.,Jin, F. , Li, JF., Lu, YJ., Wu, C.*(2008). How Are Insoluble Blocks Interacted with and Packed Inside a Micelle Made of Block Copolymers in a Selective Solvent? Macromolecules, 41(21), 8220.
PUBLICATIONS-2007
- Jin, F. *, Ye, XD., Wu, C. (2007). Observation of kinetic and structural scalings during slow coalescence of nanobubbles in an aqueous solution. J. Phys. Chem. B, 111(46), 13143.
- Jin, F. , Li, JF, Ye, XD., Wu, C.*(2007). Effects of pH and ionic strength on the stability of nanobubbles in aqueous solutions of α-cyclodextrin. J. Phys. Chem. B, 111(40), 11745.
- Jin, F. , Ye, J., Hong, LZ., Wu, C.*(2007). Slow relaxation mode in mixtures of water and organic molecules: Supramolecular structures or nanobubbles? J. Phys. Chem. B, 111(9), 2255.
- Huo, H., Jin, F. , Ngai, T.*(2007). Structure and kinetics of cluster decomposition of polystyrene star chains in dilute solutions. Macromolecules, 40(19), 6796.
PUBLICATIONS-2006
- Jin, F. , Wu, C.* (2006). Observation of first order transition in ultra-filtration of flexible linear polymer chains. Phys. Rev. Lett. , 96, 237801.
PUBLICATIONS-2005
- Jin, F. , Wu, C.* (2005). The observation of first order transition in ultra-filtration of flexible linear polymer chains. Act. Poly. Sci. , 4, 486.
PUBLICATIONS-2004
- Yang, C., Kizhakkedathu, JN., Brooks, DE., Jin, F. , Wu, C.* (2004). Laser-light-scattering study of internal motions of polymer chains grafted on spherical latex particles. J. Phys. Chem. B, 108, 18479.
TEAM
RESEARCH
GRANT/SPONSORS
- 中国科学院拨款298万,“光遗传单细胞连续定向进化仪”(2021.1-2022.12,YJKYYQ20200033,在研)
- 国家科学技术部拨款1836万,“鲁棒型人工基因元器件的设计原理与应用”(2020.7-2025.6,首席科学家,2020YFA0906900,在研)
- 国家科学技术部拨款420万,“抗瘤菌基因线路设计与合成”(2019.7-2024.6,子课题1,2018YFA0902701,在研)
- 国家基金委面上基金拨款64万,“新显微活细胞微操方法的建立以及在细菌生物被膜研究中的应用”(2018.1-2021.12,21774117,在研)
- 长安私人资本拨款200万,“ArtB项目”(2017.8-2020.8,结题)
- 国家基金委优秀青年科学基金拨款130万,“高分子表征新方法的建立和应用”(2016.1-2018.12,21522406,结题)
- 国家基金委面上基金拨款92万,“铜绿假单胞菌胞外聚合物性质及功能的高通量原位研究”(2015.1-2018.12,21474098,结题)
- 教育部博导基金拨款12万,“环境刺激响应微凝胶粒子在油水界面稳定、解稳定微观机制”(2013.1-2015.12,20133402110034,结题)
- 国家基金委面上基金拨款85万,“铜绿假单胞菌在高分子界面上的运动、感知机制研究”(2013.1-2016.12,21274141,结题)
- 国家基金委青年基金拨款25万,“高分子胶体粒子在二维油水界面上的挤阻转变”(2012.01-2014.12,21104071,结题)
PROGRESS
-
-
揭示细菌频率调制信号处理的物理原理,拓展合成生物学设计新维度
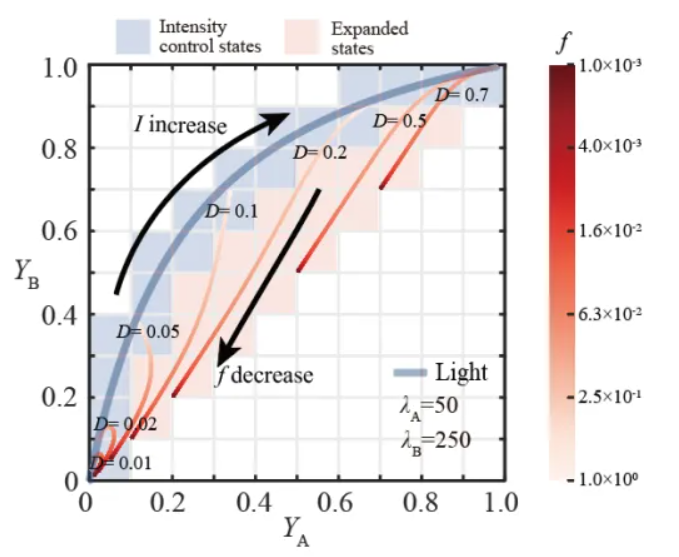 细菌能够通过频率调制(FM)信号解码机制,在三基因调控系统中将信息熵相比传统振幅调制提升约2个比特,实现了对多基因系统更加精细的调控。该研究建立了细菌频率信号处理(Frequency Amplitude Converter, FAC)的完整物理学框架,揭示了自然界中广泛存在的振荡信号背后的数学原理,为合成生物学电路设计开辟了新的维度。
细菌能够通过频率调制(FM)信号解码机制,在三基因调控系统中将信息熵相比传统振幅调制提升约2个比特,实现了对多基因系统更加精细的调控。该研究建立了细菌频率信号处理(Frequency Amplitude Converter, FAC)的完整物理学框架,揭示了自然界中广泛存在的振荡信号背后的数学原理,为合成生物学电路设计开辟了新的维度。揭示细菌信号传递的定量规律,助力人工合成细胞生命设计
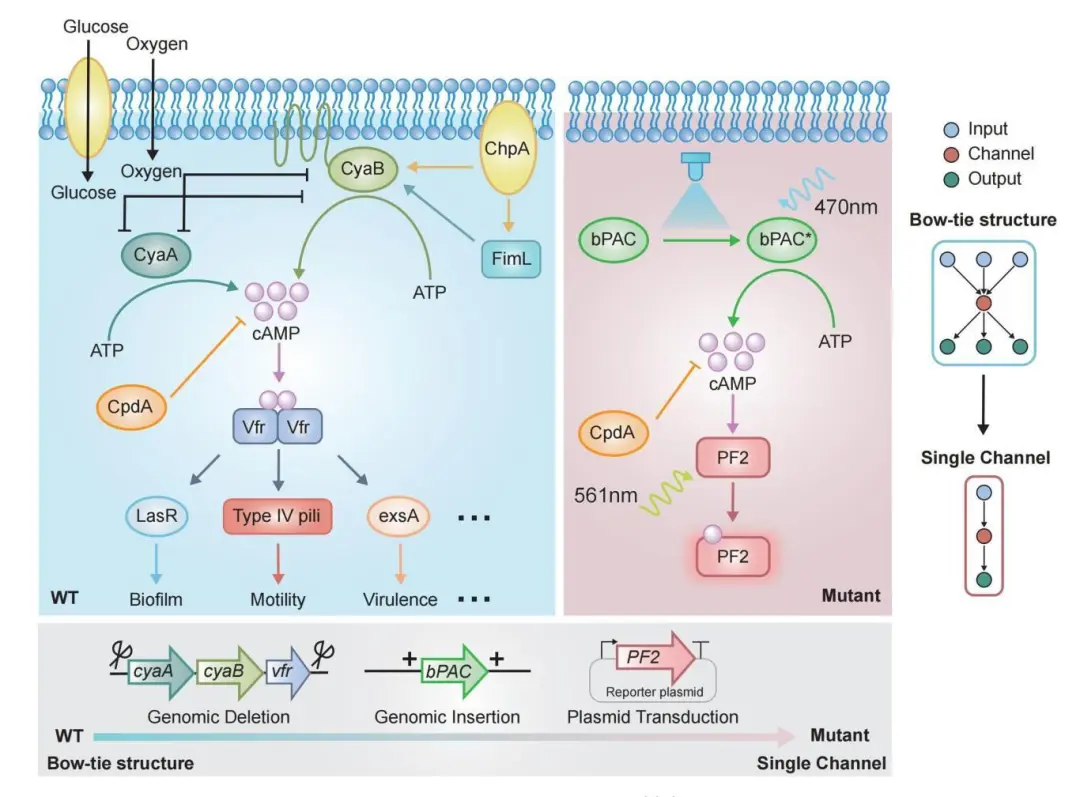 在微生物对环境信号作出细胞决策(cellular decision-making)的过程中,二级信使分子作为一种关键的中介,能够将外界刺激(初级信号)传递至下游目标,从而在信号传递中发挥至关重要的作用。然而,如何以定量化的方式深入探究这些分子在信息传递过程中的能力,仍是一个亟待解决的科学问题。
在微生物对环境信号作出细胞决策(cellular decision-making)的过程中,二级信使分子作为一种关键的中介,能够将外界刺激(初级信号)传递至下游目标,从而在信号传递中发挥至关重要的作用。然而,如何以定量化的方式深入探究这些分子在信息传递过程中的能力,仍是一个亟待解决的科学问题。基于显微镜的可用于基因元件高通量定量表征的新技术
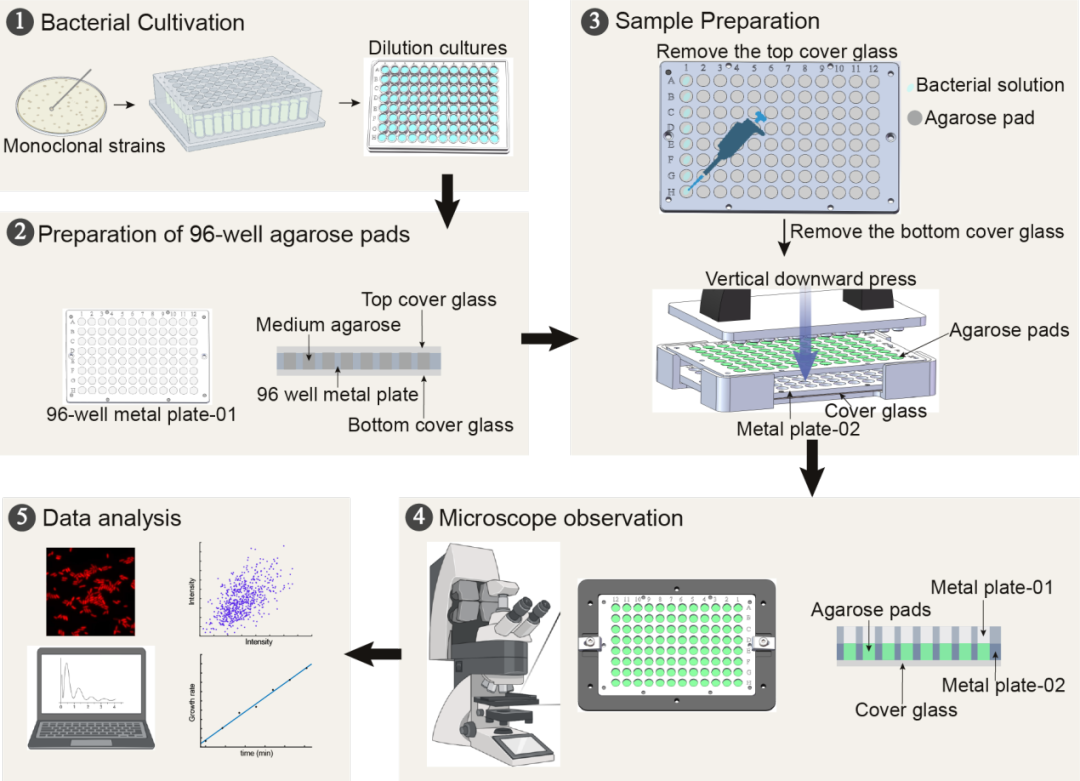 我们开发了一种创新的高通量显微平台,旨在加速基因元件的筛选和表征。该平台涉及到的专用设备也是课题组独立设计研发,解决了实验中样本准备瓶颈的问题,它具有高通量、自动化和快速扫描的特点,从样品制备到数据的自动化采集可在30分钟内完成,使得样本的准备和筛选变得更加高效。同时还可以在单细胞水平上进行了详细的分析,包括对生长速率等细胞特征的测量,为研究提供了更为全面的数据。
我们开发了一种创新的高通量显微平台,旨在加速基因元件的筛选和表征。该平台涉及到的专用设备也是课题组独立设计研发,解决了实验中样本准备瓶颈的问题,它具有高通量、自动化和快速扫描的特点,从样品制备到数据的自动化采集可在30分钟内完成,使得样本的准备和筛选变得更加高效。同时还可以在单细胞水平上进行了详细的分析,包括对生长速率等细胞特征的测量,为研究提供了更为全面的数据。构建可持续生产并精确递送靶向铜绿假单胞菌药物工程菌株
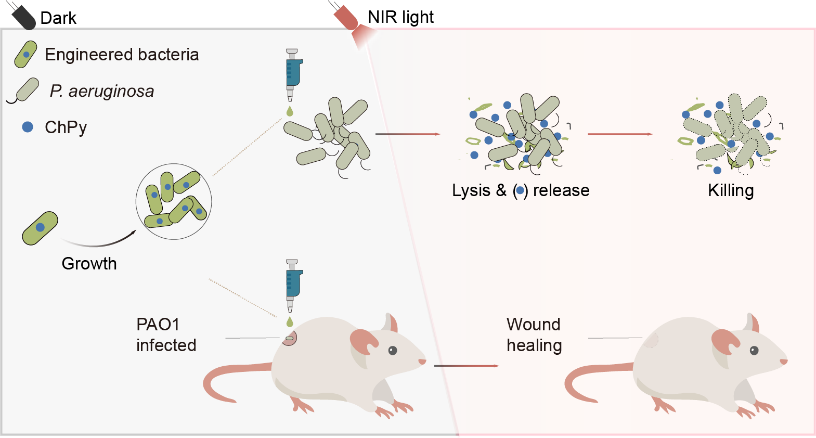 在全球范围内,由铜绿假单胞菌引发的感染通常与高死亡率相关。铜绿假单胞菌自身对很多常用的抗生素并不敏感,还会通过生成生物被膜、基因突变和水平基因转移等方法快速对新抗生素建立耐药。新抗生素的开发速度缓慢、抗生素的滥用和过度使用等因素均加速了现有的抗生素危机。开发非抗生素类药物或疗法来替代或减少抗生素的使用对提高铜绿假单胞菌感染治疗效果和缓解抗生素危机至关重要。随着合成生物学技术和元件库的不断发展,基于细菌的工程菌疗法在治疗铜绿假单胞菌感染领域具有巨大的应用前景。研究者可根据实际需求自定义益生菌、病原菌等各类细菌的功能,并可利用活细菌原位生成和精确递送药物到达的特定组织和部位。
在全球范围内,由铜绿假单胞菌引发的感染通常与高死亡率相关。铜绿假单胞菌自身对很多常用的抗生素并不敏感,还会通过生成生物被膜、基因突变和水平基因转移等方法快速对新抗生素建立耐药。新抗生素的开发速度缓慢、抗生素的滥用和过度使用等因素均加速了现有的抗生素危机。开发非抗生素类药物或疗法来替代或减少抗生素的使用对提高铜绿假单胞菌感染治疗效果和缓解抗生素危机至关重要。随着合成生物学技术和元件库的不断发展,基于细菌的工程菌疗法在治疗铜绿假单胞菌感染领域具有巨大的应用前景。研究者可根据实际需求自定义益生菌、病原菌等各类细菌的功能,并可利用活细菌原位生成和精确递送药物到达的特定组织和部位。利用近红外光编程细菌全局表型强化实体瘤治疗效果
通过合成生物学的设计,研究人员成功地将铜绿假单胞菌菌株改造成为具有实体瘤治疗功效的工程菌。在治疗过程中,该工程菌的全局表型可被近红外光的辐照程序精确的控制,即:在弱定殖、定殖以及裂解释药三种表型切换,从而更有效的消融瘤体达到治疗效果,具有巨大的潜在应用价值。
详细报道:将铜绿假单胞菌菌株改造成为具有实体瘤治疗功效的工程菌检测转录因子结合位点的新方法
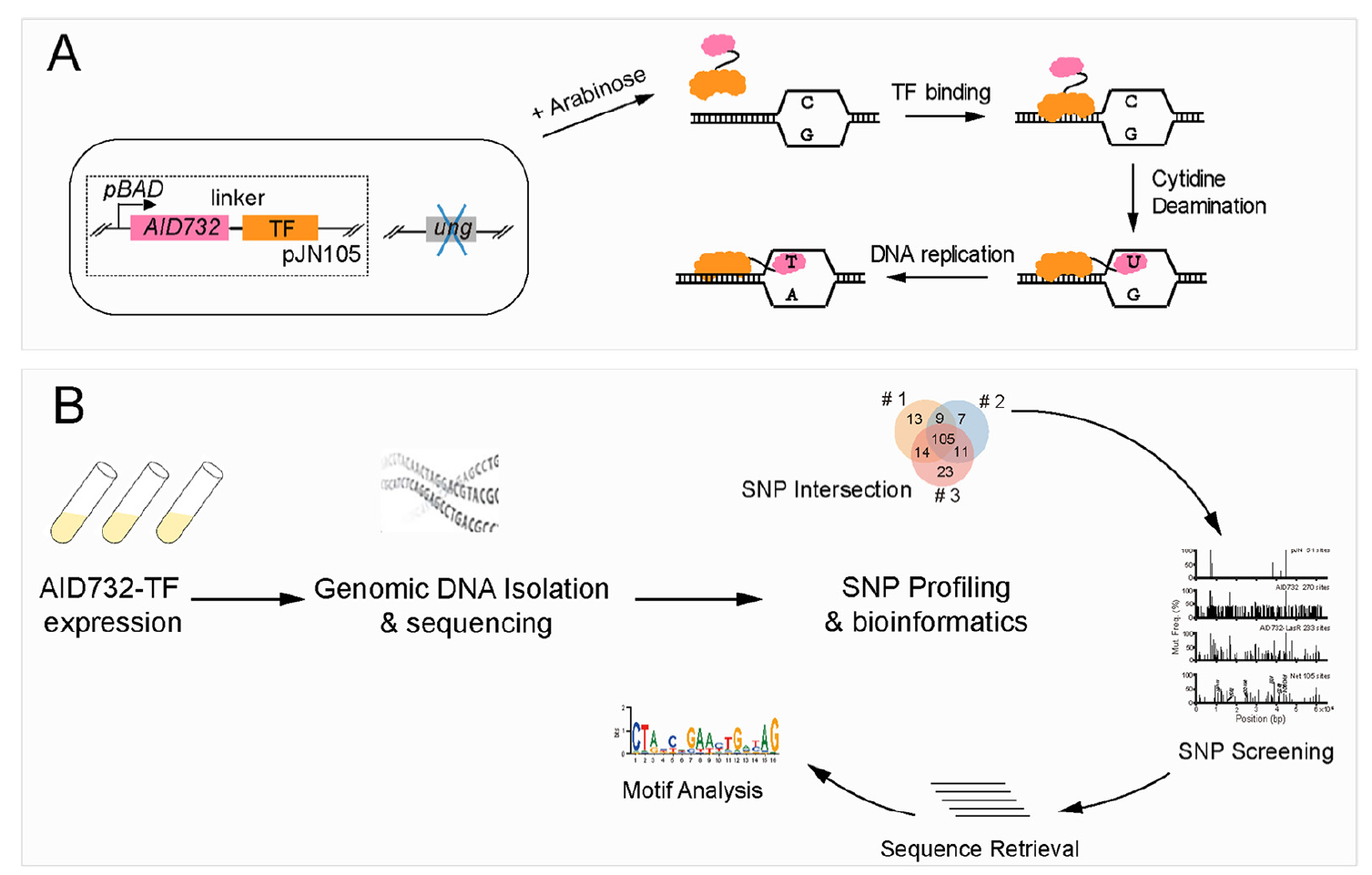 我们发展了一种检测转录因子结合位点的新方法,通过诱导转录因子-胞嘧啶脱氨酶融合蛋白表达、高通量测序和单核苷酸多态性分析,获得转录因子的全基因组结合位点信息。AIDmut-Seq不需要对转录因子结合的片段进行捕获富集,而仅需对突变标记进行测序,因此AIDmut-Seq的整个工作流程仅包含细菌培养、基因组提取和生信分析三个步骤,不涉及其他复杂的实验操作,大大节省了实验人员的时间和劳动成本。
我们发展了一种检测转录因子结合位点的新方法,通过诱导转录因子-胞嘧啶脱氨酶融合蛋白表达、高通量测序和单核苷酸多态性分析,获得转录因子的全基因组结合位点信息。AIDmut-Seq不需要对转录因子结合的片段进行捕获富集,而仅需对突变标记进行测序,因此AIDmut-Seq的整个工作流程仅包含细菌培养、基因组提取和生信分析三个步骤,不涉及其他复杂的实验操作,大大节省了实验人员的时间和劳动成本。基因组层面测量铜绿假单胞菌的转录调控噪声
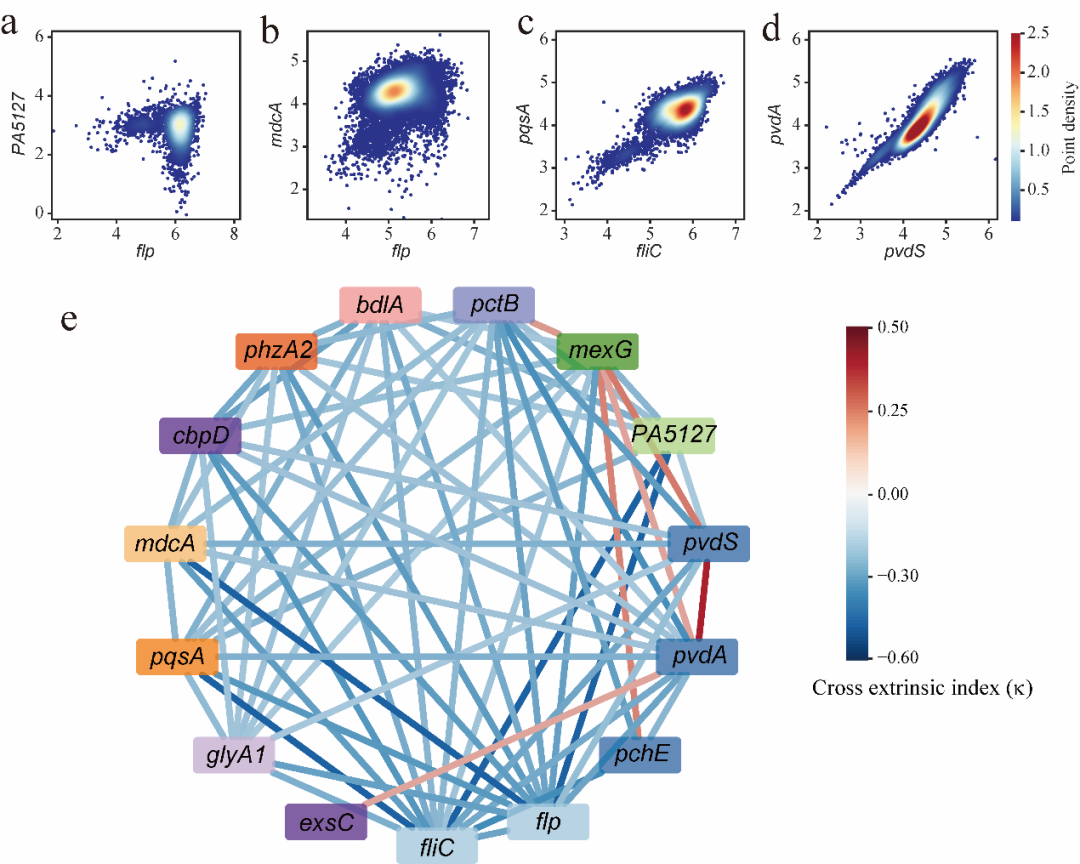 我们在模式致病菌铜绿假单胞菌中构建了一个包含3336个菌种的双色荧光转录报告系统文库,并利用文库在单细菌层次上全面分析了铜绿假单胞菌基因组中超过90%启动子的转录调控噪声。该研究提供了丰富的铜绿假单胞菌在单细胞层次上转录调控噪声的实验数据,增加了对铜绿假单胞菌种群个体差异化的理解,为探究和理解细菌如何适应复杂的生活环境提供了数据支持。
我们在模式致病菌铜绿假单胞菌中构建了一个包含3336个菌种的双色荧光转录报告系统文库,并利用文库在单细菌层次上全面分析了铜绿假单胞菌基因组中超过90%启动子的转录调控噪声。该研究提供了丰富的铜绿假单胞菌在单细胞层次上转录调控噪声的实验数据,增加了对铜绿假单胞菌种群个体差异化的理解,为探究和理解细菌如何适应复杂的生活环境提供了数据支持。光遗传工具在控制细菌行为方面的应用
 该综述首先介绍了光遗传系统的作用机理。以天然的光感受器(光敏蛋白)作为模板,通过突变、结构域互换或与其他蛋白质的模块化组合等方法可以构建出响应不同波长的光遗传系统。其次阐述了光遗传系统在转录层级和翻译后层级上的作用机理。最后综述了使用各类光遗传系统对细菌的新陈代谢、分裂、死亡、运动及生物被膜形成等行为的调控。
该综述首先介绍了光遗传系统的作用机理。以天然的光感受器(光敏蛋白)作为模板,通过突变、结构域互换或与其他蛋白质的模块化组合等方法可以构建出响应不同波长的光遗传系统。其次阐述了光遗传系统在转录层级和翻译后层级上的作用机理。最后综述了使用各类光遗传系统对细菌的新陈代谢、分裂、死亡、运动及生物被膜形成等行为的调控。自适应跟踪照明系统实现单细菌行为的控制
 我们建立了一种在单细胞水平上精确操纵铜绿假单胞菌的基因表达和细菌行为的光遗传控制方法,自适应跟踪照明(adaptive tracking illumination, ATI)系统。该方法通过将空间光调制器的图案投影到高倍油镜的视场中,实现高精度的显微镜微投影。计算机再将获取到的显微镜明场图像经过实时地图像分割和细菌识别,获取细菌的实时轮廓及位置,通过反馈算法将细菌的轮廓投影到显微镜的视场中,实现对单细菌的精确光刺激。进一步结合实时的细菌追踪算法实现对目标细菌进行连续的光刺激,从而达到精确和持续地操纵运动和分裂的单细胞行为。
我们建立了一种在单细胞水平上精确操纵铜绿假单胞菌的基因表达和细菌行为的光遗传控制方法,自适应跟踪照明(adaptive tracking illumination, ATI)系统。该方法通过将空间光调制器的图案投影到高倍油镜的视场中,实现高精度的显微镜微投影。计算机再将获取到的显微镜明场图像经过实时地图像分割和细菌识别,获取细菌的实时轮廓及位置,通过反馈算法将细菌的轮廓投影到显微镜的视场中,实现对单细菌的精确光刺激。进一步结合实时的细菌追踪算法实现对目标细菌进行连续的光刺激,从而达到精确和持续地操纵运动和分裂的单细胞行为。光遗传方法在宿主体内控制细菌致病能力
 我们基于院内感染中常见的机会性致病菌铜绿假单胞菌的GacS-GacA双组分系统,开发了新型光敏蛋白YGS24。GacS-GacA双组分系统在铜绿假单胞菌急性和慢性感染模式的切换上起到关键性的调控作用,是Gac/Rsm全局调控网络的核心的上游元件。以YGS24取代细菌中原有的GacS蛋白,就能对该细菌的感染行为进行精确的光调控。在秀丽隐杆线虫致病模型中,作者成功利用蓝光提高了细菌的致病能力。此外,利用显微镜和微流控技术,作者成功地对线虫肠道内的铜绿假单胞菌的致病通路进行了光调控。此光遗传学技术的建立,可以实现对宿主体内细菌致病能力的定量和时间控制,从而可以揭示其局部和系统对宿主健康和死亡的影响。更进一步,新的技术的建立有望探索和发现致病菌新的致病机理,进而加速相关创新疗法的开发。
我们基于院内感染中常见的机会性致病菌铜绿假单胞菌的GacS-GacA双组分系统,开发了新型光敏蛋白YGS24。GacS-GacA双组分系统在铜绿假单胞菌急性和慢性感染模式的切换上起到关键性的调控作用,是Gac/Rsm全局调控网络的核心的上游元件。以YGS24取代细菌中原有的GacS蛋白,就能对该细菌的感染行为进行精确的光调控。在秀丽隐杆线虫致病模型中,作者成功利用蓝光提高了细菌的致病能力。此外,利用显微镜和微流控技术,作者成功地对线虫肠道内的铜绿假单胞菌的致病通路进行了光调控。此光遗传学技术的建立,可以实现对宿主体内细菌致病能力的定量和时间控制,从而可以揭示其局部和系统对宿主健康和死亡的影响。更进一步,新的技术的建立有望探索和发现致病菌新的致病机理,进而加速相关创新疗法的开发。用光学方法控制细菌的运动行为
 我们在铜绿假单胞菌底盘上引入了光敏性的cAMP合成酶,经过一系列改造,构建得到一种工程菌株(命名为pactm)。该工程菌株可以响应蓝光的照射而可逆地改变自身蹭行运动的活性以及对宿主的感染能力。在蓝光照射下,pactm的cAMP应答启动子表达量增加了15倍,蹭行运动活性增加了8倍。裸鼠皮下感染模型显示,蓝光照射使pactm感染引起的小鼠皮肤损伤面积增加了14倍,因此这一工作为可控感染实验模型的构建提供了一个解决方法。此外,作者还通过宏观的光照模式设计,成功实现了对细菌群体扩张方向的引导,为研究微生物之间的相互作用提供了便利。
我们在铜绿假单胞菌底盘上引入了光敏性的cAMP合成酶,经过一系列改造,构建得到一种工程菌株(命名为pactm)。该工程菌株可以响应蓝光的照射而可逆地改变自身蹭行运动的活性以及对宿主的感染能力。在蓝光照射下,pactm的cAMP应答启动子表达量增加了15倍,蹭行运动活性增加了8倍。裸鼠皮下感染模型显示,蓝光照射使pactm感染引起的小鼠皮肤损伤面积增加了14倍,因此这一工作为可控感染实验模型的构建提供了一个解决方法。此外,作者还通过宏观的光照模式设计,成功实现了对细菌群体扩张方向的引导,为研究微生物之间的相互作用提供了便利。其他相关报道:https://phys.org/news/2021-05-strain-optically-bacteria-movement-behavior.html
合成基因线路帮助精确定量细菌中的基因重排事件
A synthetic genetic circuit to quantify repeat deletion in bacteria
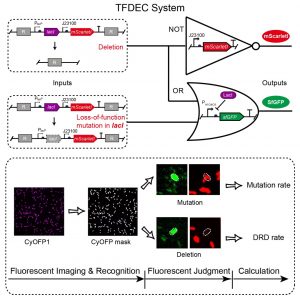
重复序列广泛地存在于原核和真核细胞基因组中,定量重复序列删除的发生率是研究DNA重排的重要手段。传统的基于抗性基因的定量方法需要引入抗生素筛选,不仅会带来较高的假阳性率,而且抗生素的引入可能影响宿主细胞的生理过程。同时,基于抗性基因的定量方法受限于抗性基因编码序列的长度,直接影响在重复序列删除率定量时对重复序列长度的定量研究。针对以上问题和原有方法的不足,我们设计了一套基因线路将DNA重排事件直接关联到不同颜色荧光蛋白的表达,再通过高通量单细菌数据采集和数据分析,就可以直接读出在细菌群体中偶发的重排事件。
饥饿使细菌生物被膜更强壮
 铜绿假单胞菌是临床中常见的一种致病菌,其生物被膜中包含的胞外多糖,外DNA,以及外分泌蛋白等共同构成了胞外聚合物。近年来,Sophie de Bentzmann等人发现在铜绿假单胞菌中过表达响应调节蛋白PprB后,四型菌毛b 、CupE菌毛、以及BapA黏附蛋白等表达的上调可共同促进一类新型超级生物被膜的形成。然而,对于PprB调节系统何时开启以及响应哪种环境信号目前尚不清楚。我们通过构建荧光报告菌株的方法对PprB下游控制相关基因的转录进行定量测量,发现铜绿假单胞菌在碳源饥饿的环境下大幅度调高了PprB下游基因的表达。
铜绿假单胞菌是临床中常见的一种致病菌,其生物被膜中包含的胞外多糖,外DNA,以及外分泌蛋白等共同构成了胞外聚合物。近年来,Sophie de Bentzmann等人发现在铜绿假单胞菌中过表达响应调节蛋白PprB后,四型菌毛b 、CupE菌毛、以及BapA黏附蛋白等表达的上调可共同促进一类新型超级生物被膜的形成。然而,对于PprB调节系统何时开启以及响应哪种环境信号目前尚不清楚。我们通过构建荧光报告菌株的方法对PprB下游控制相关基因的转录进行定量测量,发现铜绿假单胞菌在碳源饥饿的环境下大幅度调高了PprB下游基因的表达。在微生物细胞体内实现多色荧光信号的同时成像
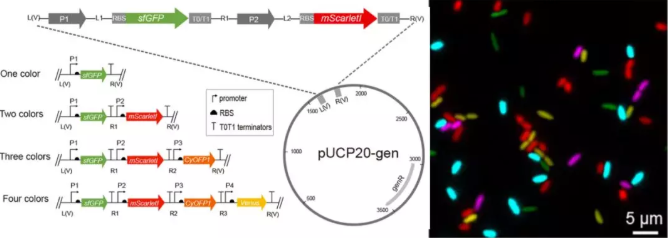 针对绝大数的信号传导系统,我们迫切需要选取多种荧光蛋白以实现对系统内上下游多个信号(大于2个)的同时检测,但光谱重叠导致会不可避免地导致不同荧光信号之间相互干扰,导致信号失真,进而无法得到可靠的数据。针对以上问题,我们提供了一套完整的多色荧光蛋白同时使用的解决方案, 包括多色荧光系统的分子生物学工具盒和多种荧光信号的精确分离算法。
针对绝大数的信号传导系统,我们迫切需要选取多种荧光蛋白以实现对系统内上下游多个信号(大于2个)的同时检测,但光谱重叠导致会不可避免地导致不同荧光信号之间相互干扰,导致信号失真,进而无法得到可靠的数据。针对以上问题,我们提供了一套完整的多色荧光蛋白同时使用的解决方案, 包括多色荧光系统的分子生物学工具盒和多种荧光信号的精确分离算法。新型显微镜技术实现对细菌“躺姿”的观测
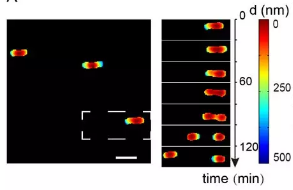
浮游状态的细菌粘附到表面是细菌生物被膜形成的第一步,而生物被膜的形成会导致致病菌介导的院内感染易反复且难以清除。因此,在细菌粘附到表面后,研究细菌的表面行为以及之间的联系有助于我们更全面、系统地了解生物被膜的形成机制和感染致病策略,并且可以为治疗细菌感染相关的临床治疗提供指导。
在单细胞水平上创建荧光计时器用以检测致病持留菌
 微生物持留菌是某个细菌群体中一定比例表型异化的小亚群,这些细菌可耐受致死浓度的抗生素作用。持留菌被认为是导致生物被膜形成和难治性感染的重要原因。在由细菌导致的生物被膜感染治疗中,抗生素可以杀死非持留的浮游菌和被膜菌,但对于生物被膜中的持留菌,抗生素不能将其完全杀灭,残存的持留菌在体内抗菌药物浓度降低或免疫力下降时可以再次引起感染,这常常会导致顽固的持续性或复发性感染。另外,持留菌在慢性感染中具有普遍而又密切的关系。因此,对持留菌的研究引起了学术界和医学界广泛的关注。
微生物持留菌是某个细菌群体中一定比例表型异化的小亚群,这些细菌可耐受致死浓度的抗生素作用。持留菌被认为是导致生物被膜形成和难治性感染的重要原因。在由细菌导致的生物被膜感染治疗中,抗生素可以杀死非持留的浮游菌和被膜菌,但对于生物被膜中的持留菌,抗生素不能将其完全杀灭,残存的持留菌在体内抗菌药物浓度降低或免疫力下降时可以再次引起感染,这常常会导致顽固的持续性或复发性感染。另外,持留菌在慢性感染中具有普遍而又密切的关系。因此,对持留菌的研究引起了学术界和医学界广泛的关注。细菌生物被膜形成的初始粘附机制
 铜绿假单胞菌 (Pseudomonas aeruginosa,PA) 是医院感染的常见条件致病菌之一, 是导致免疫功能不全病人发生感染的常见致病菌。铜绿假单胞菌介导的院内感染易反复且难以清除,主要原因是其能形成生物被膜 (biofilms)。生物被膜是由细菌及其分泌的保外基质组成,生物被膜的形成可以保护细菌免受物理、化学或机体免疫反应的攻击。因此,更深层地理解生物被膜的形成过程对如何应对铜绿假单胞菌感染具有极其重要的临床指导意义。
铜绿假单胞菌 (Pseudomonas aeruginosa,PA) 是医院感染的常见条件致病菌之一, 是导致免疫功能不全病人发生感染的常见致病菌。铜绿假单胞菌介导的院内感染易反复且难以清除,主要原因是其能形成生物被膜 (biofilms)。生物被膜是由细菌及其分泌的保外基质组成,生物被膜的形成可以保护细菌免受物理、化学或机体免疫反应的攻击。因此,更深层地理解生物被膜的形成过程对如何应对铜绿假单胞菌感染具有极其重要的临床指导意义。对活细菌生物被膜的生物打印
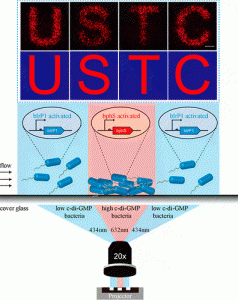 近年来,生物打印技术越来越多地应用到生物材料与再生医学领域,。利用生物打印技术打印活的哺乳动物细胞也因其在组织工程与再生医学、药物研发甚至癌症治疗等的广泛应用而越来越受到关注。不同于哺乳动物细胞,细菌常能形成致密的生物被膜而表现出极强的生存能力,而不同微生物形成的生物被膜能够生产不同的功能生物高分子,降解特定的有机化合物,例木醋杆菌在气液界面生产的细菌纤维素广泛应用于医学植入体;恶臭假单胞菌能够降解诸如苯及其衍生物而应用于污水处理。因此对活生物被膜的生物打印来获取生物被膜功能材料成为了重要的研究课题。
近年来,生物打印技术越来越多地应用到生物材料与再生医学领域,。利用生物打印技术打印活的哺乳动物细胞也因其在组织工程与再生医学、药物研发甚至癌症治疗等的广泛应用而越来越受到关注。不同于哺乳动物细胞,细菌常能形成致密的生物被膜而表现出极强的生存能力,而不同微生物形成的生物被膜能够生产不同的功能生物高分子,降解特定的有机化合物,例木醋杆菌在气液界面生产的细菌纤维素广泛应用于医学植入体;恶臭假单胞菌能够降解诸如苯及其衍生物而应用于污水处理。因此对活生物被膜的生物打印来获取生物被膜功能材料成为了重要的研究课题。细菌界的雷锋是怎么逆袭的?

绿脓杆菌中合作演化稳定的机制
光照控制的方法瓦解顽固细菌生物膜
 一般人体在感染致病细菌后,体内的免疫细胞会释放出氧化剂破坏细菌的结构并使之死亡,再利用吞噬作用将其消化。人类利用抗生素来杀死游离态细菌能做到得心应手,然而,一旦细菌形成生物膜,传统的方法就失去了效用,严重的院内感染便由此而来,病人往往无药可救。所以生物膜的调控是与人类生活息息相关的重要课题。
一般人体在感染致病细菌后,体内的免疫细胞会释放出氧化剂破坏细菌的结构并使之死亡,再利用吞噬作用将其消化。人类利用抗生素来杀死游离态细菌能做到得心应手,然而,一旦细菌形成生物膜,传统的方法就失去了效用,严重的院内感染便由此而来,病人往往无药可救。所以生物膜的调控是与人类生活息息相关的重要课题。
-
JOIN US
本实验室长期招收对合成生物学感兴趣的博士后,研究助理,及客座学生,不限专业背景(数学、物理、化学、生物、工程)。
联系方式
fan.jin@siat.ac.cn
Phone
+86 0755-26409621
Address
1068 Xueyuan Boulevard.
University Town of Shenzhen,
Nanshan, Shenzhen 5180551
China
Combination of Synthetic Biology and Quantitative Biology
i. Redesign the Light Path and Build Microscope
INTRODUCTION
Bacteria are the smallest micro-organisms, ranging from between 0.0001 and 0.001 mm in size. Phytoplankton and protozoa range from about 0.001 mm to about 0.25 mm. The largest phytoplankton and protozoa can be seen with the naked eye, but most can only been seen under a microscope.
ii. Arithmetic Operations
INTRODUCTION
Mathematical biology is the work that uses mathematical approaches to gain biological understanding or explain biological phenomena. The most fundamental branch of math is arithmetic operations. Applying arithmetic operations to biology, providing biological insight as a result of mathematical analysis or identify and open up challenging new types of mathematical problems that derive from biological knowledge (in the form of data, or theory, or simulation results).
iii. Mathematical Modeling
INTRODUCTION
Mathematical models allow researchers to investigate how complex regulatory processes are connected and how disruptions of these processes may contribute to the development of disease. In addition, computational models help investigators to systematically analyze systems perturbations, develop hypotheses to guide the design of new experimental tests, and ultimately assess the suitability of specific molecules as novel therapeutic targets.
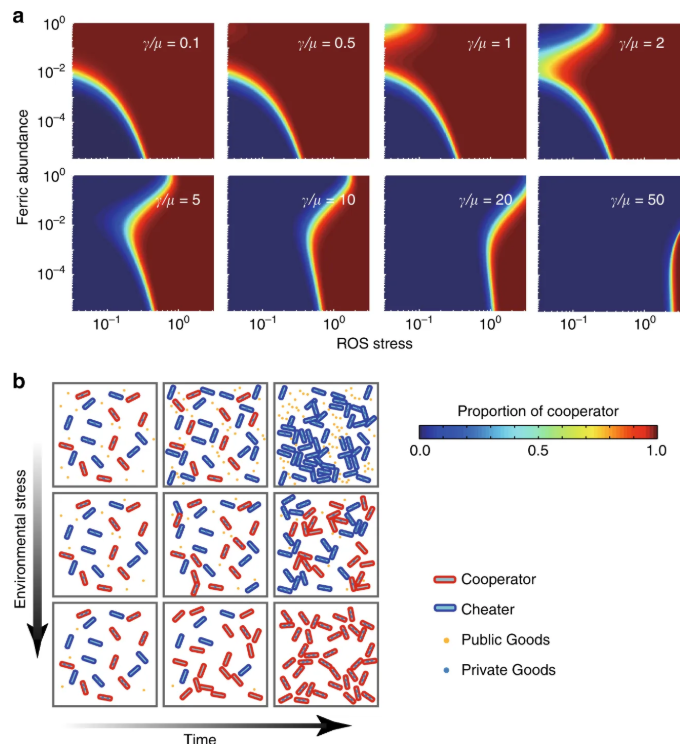
Precise Regulation of the Phenotype of Bacteria at Single-cell Level and its Application in Synthetic Biology
i. Optogentics
INTRODUCTION
Light has advantages over chemical means as it acts noninvasive, has low toxicity and most crucial, provides superior spatial and temporal resolution. Optogenetic approaches opened up a new era in neurobiology which controlling and monitoring the activities of individual animal neurons using optogenetic actuators like channelrhodopsin, halorhodopsin, and archaerhodopsin. Moreover, this technique has been shown to extend outside neurons to other field of biology. Modern optogenetics have been defined as the combination of genetic and optical methods to cause or inhibit prescriptive events in specific cells of living tissue and behaving animals.
Bioprinting Living Biofilms through Optogenetic Manipulation
ii. Bacterial Therapy of Cancer
INTRODUCTION
Bacteria have been explored as cancer treatments for over a century. Here, we focus specifically on the application of synthetic biology in bacteria to engineered bacterial cancer therapies, highlighting major instances of engineering.
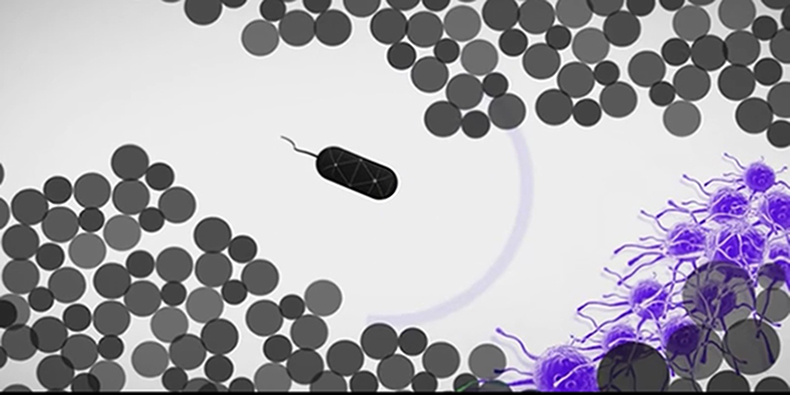
iii. Interaction between Bacteria and the Host
INTRODUCTION
The host-pathogen interaction is defined as how microbes or viruses sustain themselves within host organisms on a molecular, cellular, organismal or population level. This term is most commonly used to refer to disease-causing microorganisms although they may not cause illness in all hosts.
PUBLICATIONS
PUBLICATIONS-2025
-
-
- Zhang, R.#, Wan, S.#, Xiong, J., Ni, L., Li, Y., Huang, Y., Li, B., Li, M., Yang, S.*, and Jin, F.*. (2025) Decoding frequency-modulated signals increases information entropy in bacterial second messenger networks. Nat. Phys. 21, 1728-1740.
- 杨帅#, 徐韵东, 金帆*. (2025) 合成生物学在医学诊疗中的应用与伦理治理:技术突破与价值边界. 合成生物学.
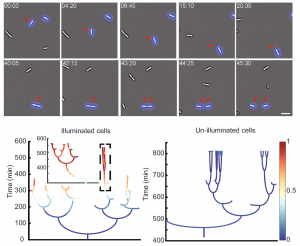
- Xiong, J.#, Wang, L.#, Lin, J.#, Ni, L., Zhang, R., Yang, S., Huang, Y., Chu, J.*, and Jin, F.*. (2025). Quantifying second-messenger information transmission in bacteria. Nat. Phys. 21, 1009–1018. Research briefing:Bacterial second messengers achieve extraordinary signal capacity
- Zhang, J.#, Luo, Y.#, Zong, Y., Lu, S., Shi, Y.*, Jin, F.* , and Zhao, K.* (2025). The role of PilU in the surface behaviors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. mLife. 2025 Feb 23; 83-95.
-
PUBLICATIONS-2023
-
-
- Zhang, R.#, Huang, Y.#, Li, M., Wang, L., Li, B., Xia, A., Li, Y., Yang, S.*, and Jin, F.*. (2023). High-throughput, microscopy-based screening and quantification of genetic elements. mLife. 2023; 1–12.
- Gao, Y.#, Wei, J.#, Fu, S., Xing, X., Zhang, R.* and Jin, F.*. (2023). Remotely Controllable Engineered Bacteria for Targeted Therapy of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infection. ACS Synth. Biol.
- Fu, S.#, Zhang, R.#*, Gao, Y., Xiong, J., Li, Y., Pu, L., Xia, A., and Jin, F.*. (2023). Programming the lifestyles of engineered bacteria for cancer therapy. Natl. Sci. Rev., nwad03.
- Cao, Z.#, Zuo, W.#, Wang, L., Chen, J., Qu, Z., Jin, F., and Dai, L*. (2023) Spatial profiling of microbial communities by sequential FISH with error-robust encoding, Nat. Commun., 14, 1477.
- 付生伟, 金帆*. (2023). 若干裂解基因盒子的表征及应用. 生物工程学报, 39(3): 1142-1162.
-
PUBLICATIONS-2022
-
-
- Li, F., Liu, X.-Y., Ni, L.*, and Jin, F.* (2022) AIDmut-Seq: a Three-Step Method for Detecting Protein-DNA Binding Specificity, Microbiol. Spectr., 0, e03783-03722.
- Chen, W.#, Zhang, J.#, Li, F.#, Wang, C., Zhang, Y., Xia, A., Ni, L.*, and Jin, F.* (2022) Genome-Wide Analysis of Gene Expression Noise Brought About by Transcriptional Regulation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa, mSystems, 0, e00963-00922.
- Xia, A.#, Zhang, R.#, Huang, Y., Ni, L., Pu, L., Li, Y., Yang, S.*, and Jin, F.* (2022) An adaptive tracking illumination system for optogenetic control of single bacterial cells, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol.,106, 6775-6784.
- Wei, J., and Jin, F.* (2022). Illuminating bacterial behaviors with optogenetics. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci., 26, 101023.
- 李飞旋, 倪磊*, 金帆*. (2022). 铜绿假单胞菌中快速基因操作工具的开发和应用. 生物工程学报, 1-15.
-
- 陈文辉, 金帆*. (2022). 铜绿假单胞菌中S型绿脓杆菌素与荧光嗜铁素的功能协同性分析. 生物工程学报, 1-26.
-
- 张亭, 冷梦甜, 金帆, 袁海*. (2022). 合成生物研究重大科技基础设施概述. 合成生物学, 3(01):184-194.
-
PUBLICATIONS-2021
-
-
- Cheng, X.#, Pu, L.#, Fu, S.#, Xia, A., Huang, S., Ni, L., Xing, X., Yang, S.*, Jin, F.* (2021). Engineering Gac/Rsm Signaling Cascade for Optogenetic Induction of the Pathogenicity Switch in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. ACS Synth. Biol., 10, 6, 1520–1530
- Xia, A., Qian, M., Wang, C., Huang, Y., Liu, Z.*, Ni, L*. Jin, F.* (2021). Optogenetic Modification of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Enables Controllable Twitching Motility and Host Infection. ACS Synth. Biol., 10, 3, 531–541.
- Wong, GCL., Yang S., Jin, F.* et al.(2021). Roadmap on emerging concepts in the physical biology of bacterial biofilms: from surface sensing to community formation. Phys. Biol., 210.75.253.170.
- 杨帅, 金帆*. (2021). 单细菌表型的高通量表征和控制. 科学通报, 66(03):367-383.
- 金帆*#, 李奉庭#, 夏霖*. (2021). CRISPR/Cas在定向进化技术中的应用. 集成技术, 10(04):33-49.
- 金帆*#, 高艳梅#, 黄亚佳, 蒲璐, 夏霖*. (2021). 铜绿假单胞菌感染治疗现状. 集成技术, 10(04):50-66.
- 辛颖#, 徐宝琪#, 王军杰#, 张荣荣#, 温慧, 王金娟, 梁帆, 金帆, 梁卓, 黄建东*, 黄术强*. (2021). 用于高分辨率成像的肺器官芯片构建及肺炎模型应用研究. 集成技术, 10(04):126-136.
-
PUBLICATIONS-2020
-
-
- Yang, S., Jin, F.* (2020). Characterization and control of bacterial phenotypes at the single cell level. Chin. Sci. Bull., 65: 1-17.
- 蒲璐, 黄亚佳, 杨帅, 金帆* (2020). 合成生物学在感染性疾病防治中的应用. 合成生物学, 1(2): 134-149.
- Huang, Y., Yang, S., Chen, W., Li, F., Xia, A., Ni, L.*, Yang G.*, Jin, F.* (2020). A synthetic genetic circuit enables precise quantification of direct repeat deletion in bacteria. ACS Synth. Biol., 9, 1041-1050.
- Cheng, Z.#, Xiong, J.#, Min, D., Cheng, L., Liu, D.*, Li, W., Jin, F., Yang, M., Yu H. (2020). Promoting bidirectional extracellular electron transfer of Shewanella oneidensis MR‐1 for hexavalent chromium reduction via elevating intracellular cAMP level. Biotechnol. Bioeng., 117, 1294-1303.
-
PUBLICATIONS-2019
-
-
- Wang, C.#, Chen, W.#, Xia, A., Zhang, R., Huang, Y., Yang, S.,Ni, L.*, Jin, F.* (2019). Carbon starvation induces the expression of PprB-regulated genes in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 85: e01705-19.
- Han, J.#, Xia, A.#, Huang, Y., Ni, L., Chen, W., Jin, Z., Yang, S.*, Jin, F.* (2019). Simultaneous Visualization of Multiple Gene Expression in Single Cells Using an Engineered Multicolor Reporter Toolbox and Approach of Spectral Crosstalk Correction. ACS Synth. Biol., 8, 2536-2546.
- Armbruster, CR., Lee, CK., Parker-Gilham, J., de Anda, J., Xia, A., Zhao, K., Murakami, K., Tseng, BS., Hoffman, LR., Jin, F.*, Harwood, CS., Wong, GCL.*, Parsek MR. * (2019). Heterogeneity in surface sensing suggests a division of labor in Pseudomonas aeruginosa populations. eLife, 8, e45084.
- Xia, A.#, Yang, S.#, Zhang, R., Ni, L., Xing, X.*,Jin, F.* (2019).Imaging the Separation Distance between the Attached Bacterial Cells and the Surface with a Total Internal Reflection Dark-Field Microscope. Langmuir, 35, 8860-8866.
- Lee, EY., Zhang, C., Di, DJ., Jin, F., Connell W., Hung, M., Malkoff, N., Veksler, V., Gilliet, M., Ren, P., Wong, GCL.* (2019). Helical antimicrobial peptides assemble into protofibril scaffolds that present ordered dsDNA to TLR9. Nat. Commu., 10(1), 1012.
- 黄亚佳, 倪磊, 金帆, 杨光*. (2019). 基于高通量显微成像及分析技术的DNA重排研究. 集成技术, 8(06):31-38.
-
PUBLICATIONS-2018
-
-
- Xia, A.#, Han, J. #, Ni, L., Yang, S.*, Jin, F.* (2018). Dual-color fluorescent timer enables detection of growth-arrested pathogentic bacterium. ACS Infect. Dis., 4, 1666.
- Yang, S.#, Cheng X.#, Jin, Z., Xia, A., Ni, L., Zhang, R., Jin, F.* (2018). Differential production of Psl in planktonic cells leads to two distinctive attaching phenotypes in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 84(14), e00700-18.
- Huang, Y.#, Xia, A.#, Yang, G.*, Jin, F.* (2018). Bioprinting Living Biofilms through Optogenetic Manipulation. ACS Synth. Biol., 7, 1195-1200.
- Jin, Z.#, Li, J.#, Ni, L., Zhang, R., Xia, A., Jin, F.* (2018). Conditional privatization of a public siderophore enables Pseudomonas aeruginosa to resist cheater invasion. Nat. Commu., 9, 1383.
- 金帆. (2018). 从“设计生命”到理解生命:对生命科学的哲学阐释. 文化纵横, 01:122-131.
-
PUBLICATIONS-2017
-
-
- Pu, L.#, Yang, S.#, Xia, A., Jin, F.* (2017). Optogenetics Manipulation Enables Prevention of Biofilm Formation of Engineered Pseudomonas aeruginosa on Surfaces. ACS Synth. Biol., 7, 200-208.
- 倪磊*,金震宇,杨帅,金帆 (2017). 铜绿假单胞菌蹭行运动单细胞分析方法的建立及应用. 生物工程学报, 33(9), 1611-1624.
- Zhang, R.#, Xia, A.#, Ni, L., Li, FX., Jin, Z., Yang, S., Jin, F.* (2017). Strong shear flow persister bacteria resist mechanical washing on the surfaces of various polymer materials. Adv. Biosyst., 1, 1700161.
- Brill-Karniely, Y., Jin, F., Wong, GCL., Frenkel, D., Dobnikar, J.* (2017). Emergence of complex behavior in pili-based motility in early stages of aeruginosa surface adaptation. Sci. Rep., 7, 45467.
-
PUBLICATIONS-2016
-
-
- Ni, L., Yang, S., Zhang, R., Jin, Z., Chen, H., Conrad, J.C.*, Jin, F.* (2016). Bacteria differently deploy type-IV pili on surfaces to adapt to nutrient availability. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes, 2, 15029.
- Cai, J., Yue, Y., Wang, Y., Jin, Z., Jin, F., Wu, C.* (2016). Quantitative study of effects of free cationic chains on gene transfection in different intracellular stages. J Control Release, 238, 71.
- Lee, EY., Lee, CK., Jin, F., Lande, R., Curk, T., Frenkel, D., Dobnikar, J., Gilliet, M., Wong, GCL.* (2016). A review of immune amplification via ligand clustering by self-assembled liquid-crystalline DNA complexes. Colloid & Interface Sci., 232, 17.
- Gao, P., Yi, Z., Xing, X., Ngai, T.*, Jin, F.* (2016). The influence of additive-free particle spreading method on interactions between charged colloidal particles at an oil/water interface. Langmuir, 32, 4909-4916.
-